Blog Layout
How Equitable Math Practices Help Students of Color with Conceputal Understanding
India White • May 1, 2023
How Equitable Math Practices Help Students of Color with Conceptual Understanding

How Equitable Math Practices Helps Students of Color with Conceptual Understanding
Dr. India White
Mathematics is a subject that is often perceived as difficult and intimidating by many students, especially those from marginalized communities. According to Chap Gpt, Students of color have historically faced systemic barriers in accessing quality math education. However, equitable math practices can help to bridge this gap and support students of diverse backgrounds in their conceptual understanding in the math classroom. This has become an area of focus, given that the White-Black population
gap of students has narrowed by 32 points from 1992 to 2017. Seeing the population of studnets is now made up of predominantly students of color, teachers are tasked with helping these students with understanding math better than before.
Here are some strategies for helping diverse learners with conceptual understanding in their math class through equitable practices: 1) Strive for inclusive learning environments, 2) Use real-world examples and culturally relevant contexts, 3) Promote collaborative learning, and 4) using multiple forms of assessment to eliminate bias and strengthen students’ skillset during assessments.
Equitable Math Practices Strive for Inclusive Learning Environments
Equitable math practices are rooted in foundational principles of social justice with a goal to create a more inclusive and accessible learning environment for all students. These practices recognize and address the various inequities that exist in math education, including the lack of representation of diverse learners in advanced level math courses, lack of diverse representation in teachers, and a lack of culturally responsive teaching methods.
How Equitable Math Practices Support Students of Color
One of the primary ways that equitable math practices support students of color is by emphasizing the importance of conceptual understanding over rote memorization. Rather than students being assigned math problems in efforts to formulas and procedures, through conceptual understanding and metacognition, students are encouraged to develop a deeper understanding of the underlying concepts and principles of math. This approach helps to build a strong foundation of mathematical knowledge that can be applied to a wide range of problems and situations.
Equitable Math Practices Use Real-World Examples to Connect Students through Culture
In their article on “Making the Connections between Culture and Mathematics , Northwestern University speaks about how equitable math practices also prioritize the use of real-world examples and culturally relevant contexts in math instruction.
By connecting math concepts to students' lived experiences and cultural backgrounds, teachers can help to make math more engaging and meaningful for students of color. This approach can also help to counteract the stereotype that math is a subject that is only relevant to certain groups of people.
Equitable Math Practices Help with Collaborative Learning
Another important aspect of equitable math practices is the use of collaborative learning strategies. By working in groups and engaging in peer-to-peer learning, students can develop a deeper understanding of math concepts and build their problem-solving skills. This approach also helps to create a more supportive and inclusive learning environment, where students feel valued and respected for their contributions.
Equitable Math Practices Strengthen Skills during Assessments
Equitable math practices also prioritize the use of multiple forms of assessment, including performance-based assessments and project-based learning.
These types of assessments allow students to demonstrate their understanding of math concepts in a variety of ways, rather than simply through traditional tests and quizzes. This approach can help to reduce the impact of cultural biases that can be found in assessment and produce a better reflection of students' mathematical abilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, equitable math practices are essential for supporting students of diverse populations in developing a deeper conceptual understanding of math. By prioritizing conceptual understanding during their learning experience, using real-world examples and culturally relevant contexts, promoting collaborative learning, and using multiple forms of assessment, teachers can create a more inclusive and accessible learning environment for all students. By implementing these practices, we can help to ensure that all students have access to explore learning in ways that will build upon their ability to conceptual understand each topic at hand.


By India White
•
April 8, 2025
Forgiveness: Walking in G.R.I.T. and Grace Forgiveness isn't for the faint of heart. It takes G.R.I.T.—Growth Mindset, Resilience, Self-Efficacy, and Time Management—to truly walk in forgiveness, especially when you've been wronged, mistreated, or misunderstood. But there's no greater example of gritty forgiveness than Jesus Himself. As He hung on the cross—suffering, bleeding, and abandoned—He didn’t curse His enemies. He didn’t demand justice in that moment. Instead, He looked toward heaven and said: “Father, forgive them, for they know not what they do” (Luke 23:34). Let that sink in. The very people who had betrayed, mocked, beaten, and crucified Him were the ones He forgave. And He did it in real time, while the pain was still fresh. That’s Great Resilience In Time. And as followers of Christ, we’re called to do the same. We’re called to forgive those who have: • Abused us—physically, emotionally, or spiritually • Slandered us behind our backs • Taken advantage of our kindness • Lied to us, hurt us, or wronged us in ways words can’t capture Forgiveness doesn’t mean the pain was okay. It doesn’t mean you return to harmful situations. But it does mean we release people into God’s hands. We stop carrying the weight of bitterness. And we trust that nobody gets by—God is just, but He is also merciful. “I did not come to call the righteous, but sinners to repentance.” — Luke 5:32 God operates in mercy—not because people always deserve it, but because His heart is for restoration. And if we want God to operate in mercy toward us, we must be willing to pray that same mercy over those who have hurt us. Hence, I want to share with you 5 Tips for Operating in Forgiveness Through G.R.I.T. and Grace: 1. Growth Mindset: Choose to Learn, Not Linger Instead of replaying the pain, ask God what He wants to teach you through it. Every hurt can become holy ground if we allow it to transform us instead of trap us. Forgiveness is a chance to grow. Even when you find yourself lingering in the memories and wondering "What if?", choose to use the moments of hurt as an opportunity to heal and evolve into a greater version of you. 2. Resilience: Bounce Back with God’s Strength Resilience doesn’t mean you don’t feel the pain—it means you refuse to let it define you. Forgiveness builds spiritual stamina. Each time you choose grace, you build strength in your spirit. The enemy wanted that trial, setback, dissapointment to cause you to give up on God and yourself. However, you must believe that no weapon formed against you shall propser. Never allow Satan to take away your song or your purpose, no matter the weapon or vessel he chooses to attack you through. 3. Self-Efficacy: Believe You Can Forgive with God’s Help Forgiveness may feel impossible—but with God, you can do all things. Self-efficacy is about believing in your ability to move forward. Speak life over yourself: "With God’s help, I can forgive." This is not always an easy process but you can do it! Choose to speak positively about your situation. Tell God that you forgive them and take moments to think about what Jesus must have felt at the cross as he died for you. Sometimes, we are made to emulate the light of Christ so that others will have HOPE. That means we must be willing to be curicifed at thier hands for the Glory of God. However, be encouraged, for the Lord will restore you. 4. Time Management: Don’t Waste Time on Bitterness Bitterness drains energy and time. Let forgiveness help you refocus your time and emotional energy toward purpose, healing, and joy. Steward your time wisely—it’s too precious to spend in bondage. Take time for self-care. Cry it out, seek therapy, have an outlet that will help you develop and heal and mature in a healthy fashion. Understand that all of us fall short; people will most likely dissapoint you, so flow in grace. 5. Great Resilience In Time: Forgive Even When It Still Hurts Forgiveness is often a process, not a one-time event. It requires Great Resilience In Time —the ability to keep choosing grace, even when the pain is fresh. Jesus forgave while He was still on the cross. We, too, can learn to forgive even while healing. Through your forgiveness you'll find revelation that will bring your closer to your heavenly Father. Forgiveness is one of the greatest gifts you can give—to others, yes, but also to yourself. It frees your heart. It releases your soul. It makes space for God to heal what others tried to break. Jesus didn’t wait for an apology. He forgave in real time—with G.R.I.T. and grace. So today, let’s strive to do the same. Let’s live with: • A growth mindset that says, “God can use even this.” • Resilience that says, “I will not be broken.” • Self-efficacy that says, “I can do this with God.” • Time management that says, “I will not waste one more second holding a grudge.” Let’s walk in Great Resilience In Time and extend the same mercy we so desperately need. Because forgiveness isn’t weakness. It’s worship. So, wipe you tears, forgive, reset, start over, and thrive through G.R.I.T. and Grace. Love, India Want more? Visit www.india-white.com to schedule a meeting or book me for an event. Want a copy of the Grit Workbook for Clergy (Pastors) Click here!

By India White
•
April 3, 2025
### April Newsletter: A Month of Grit and Growth April is here, and it’s shaping up to be an exciting month filled with powerful opportunities to build grit, inspire educators, and impact students. From conferences to new resources, I’m thrilled to share what’s happening this month and how you can get involved. Speaking at MCTM’s Annual Math Conference in Minnesota I’m honored to present at the Minnesota Council of Teachers of Mathematics Annual Conference this month, where I’ll be diving into how to create a Gritty Thinking Classroom. In this session, we’ll explore how the G.R.I.T. framework aligns with Peter Liljedahl’s Building Thinking Classrooms, helping educators develop a culture of perseverance, resilience, and self-efficacy in their math students. If you’re attending, I’d love to connect and discuss ways to empower students through productive struggle. G.R.I.T. Workbooks and Resources The G.R.I.T. Workbook series continues to grow, providing teachers, students, and parents with practical tools to develop growth mindset, resilience, and time management. Whether you’re looking to strengthen your own grit or help students push through challenges, these workbooks offer actionable strategies to build confidence and perseverance. G.R.I.T. Online Courses and Masterclass For those looking to take a deeper dive into grit, we’re rolling out G.R.I.T. online courses and mini-workshops designed to help educators and leaders implement grit-based strategies in their schools and classrooms. Stay tuned for our Masterclass, which will provide an interactive learning experience on how to cultivate grit in both personal and professional settings. G.R.I.T. Podcast: Conversations That Inspire The G.R.I.T. Podcast continues to feature insightful conversations with educators, leaders, and changemakers who are passionate about building perseverance and resilience. Each episode offers motivation and strategies to help you stay committed to your goals and push through challenges. Be sure to tune in for inspiring discussions that fuel personal and academic growth. Stay Connected If you’re looking for more ways to engage with the G.R.I.T. movement, be sure to check out: - www.india-white.com – Explore my work, speaking engagements, and resources - www.gritacademy.us – Learn about G.R.I.T. Academy, where we help students and educators develop the skills they need to thrive This month is all about embracing grit, growth, and resilience. Whether through conferences, podcasts, or online learning, I’m excited to continue this journey with you. Let’s keep pushing forward and building a culture of perseverance together. Stay gritty and keep striving for greatness!

By India White
•
April 3, 2025
Excited to Speak at MCTM’s Annual Math Conference: Building a Gritty Thinking Classroom! I can’t wait to present at MCTM’s Annual Math Conference this April in Minnesota. This opportunity is truly special because I’ll be diving into two of my passions—grit and Building Thinking Classrooms—to help educators create Gritty Thinking Classrooms that foster resilience, problem-solving, and perseverance in students. Why Grit Matters in the Math Classroom Math is not just about numbers and equations; it’s about persistence, self-efficacy, and growth mindset. So many students struggle with productive struggle, but when we intentionally build grit, they learn how to push through challenges rather than give up. By implementing Dr. India White’s G.R.I.T. framework, we help students: - Develop a growth mindset - Build resilience in problem-solving - Strengthen self-efficacy - Improve time management and perseverance Connecting Grit with Building Thinking Classrooms Peter Liljedahl’s Building Thinking Classrooms has transformed the way we engage students in math learning. When we merge BTC structures with grit, we create an environment where students: - Tackle challenging problems head-on - Collaborate with peers to build understanding - Learn to embrace struggle as part of growth - Develop confidence in their ability to succeed In my session, we’ll explore how BTC’s 14 elements align with grit and how teachers can create a culture of perseverance in their classrooms. See You in Minnesota! If you’re attending MCTM’s Annual Math Conference, I’d love to connect. Let’s talk about how to empower students to think, struggle, and grow. Together, we can build Gritty Thinking Classrooms that transform how students learn and engage with mathematics. Let’s get gritty! See you soon in Minnesota!

By India White
•
March 25, 2025
🌟 Excited to share my VCTM recap video! 🎥 Join me as I engage with teachers during my keynote, discussing strategies to best support our 8th grade math students. Together, we can make a difference! 💪📚 Check it out and let’s keep the conversation going! #drindiawhite #nctm #ncsm #vctm #vermont #nabse #naacp #education #doe

By India White
•
March 25, 2025
Reflection on The Power of Grit Keynote to Vermont Teachers Speaking to the dedicated educators of Vermont about the Power of Grit was an inspiring and reaffirming experience. As I shared the pillars of grit—Growth Mindset, Resilience, Time Management, and Self-Efficacy—it was evident that these concepts resonated deeply with the teachers in the room. Their commitment to fostering perseverance and confidence in their students was both heartening and energizing. Throughout the keynote, I emphasized the transformative role of a growth mindset—how students who embrace challenges and see effort as a path to mastery are more likely to persist through difficulties. I could see educators nodding in agreement as they reflected on their own students' struggles and triumphs. Encouraging students to reframe failure as a learning opportunity is a crucial shift that builds not just better mathematicians, writers, and thinkers but also more resilient individuals. Resilience was another cornerstone of the discussion. I shared stories and strategies to help students push past obstacles and develop the endurance needed to navigate academic and personal challenges. The engagement in the room reaffirmed that teachers, too, are models of resilience, especially in today’s educational climate. One of the most practical elements of the keynote focused on time management—helping students (and educators) break down overwhelming tasks, set realistic goals, and prioritize effectively. The response to this section showed that time management remains a crucial skill, not only for students learning to structure their studies but also for teachers juggling multiple responsibilities. Finally, we explored the power of self-efficacy, that deep-seated belief that one’s efforts lead to success. We discussed ways to cultivate this mindset in students through intentional feedback, scaffolding, and celebrating small wins. Seeing the teachers reflect on how they could implement these strategies in their classrooms was incredibly rewarding. This keynote reaffirmed my belief that grit is not just a personal trait—it’s a culture that educators can foster in their classrooms, schools, and communities. Vermont’s educators left the session with new insights, actionable strategies, and a renewed commitment to equipping students with the perseverance and confidence needed for success. I am grateful for the opportunity to share this message, and I look forward to seeing the impact of their work in cultivating grit across the state. Thanks Vermont Rockstars. Stay gritty!
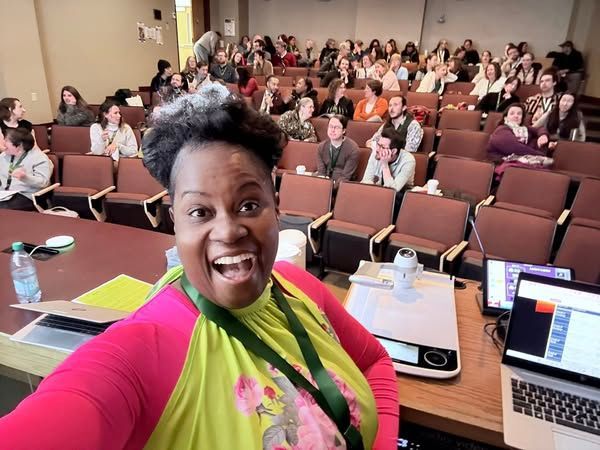

By India White
•
March 25, 2025
✨ I had a phenomenal time speaking for the VCTM Rockstars in Vermont! We dove into how to reach all learners and stay motivated through grit. 💪 I can't wait to see the results from the grit assessment and framework! Stay gritty, y’all! 🌟 #drindiawhite #vctm #vermont #grit #educators #math
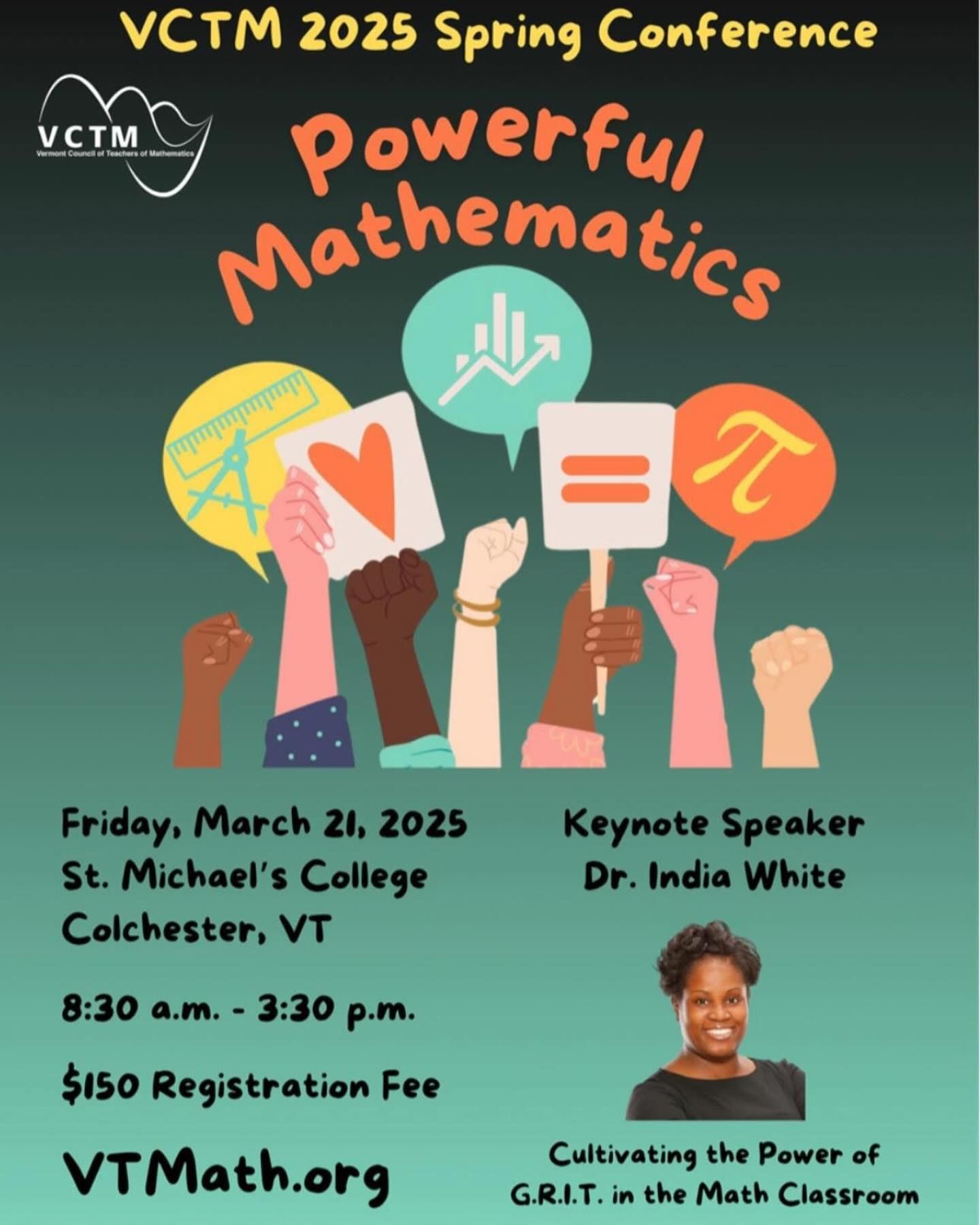
By India White
•
March 18, 2025
🌟 Super excited to announce that I’ll be the keynote speaker at the VCTM Annual Conference in beautiful Vermont! 🎉 Huge thanks to the amazing VCTM rockstars for this incredible opportunity! Let’s dive into the power of grit together! 💪✨ I can’t wait to share insights and connect with fellow educators, students, and math enthusiasts. Join us by registering below: https://vctm.wildapricot.org/event-5950535 Let’s make this an unforgettable experience! #drindiawhite #grit #tedx #vctm #teachers #students #math (I don’t own music copyright)

By India White
•
March 18, 2025
Join us on the Let's Get Gritty Podcast with Dr. India White, featuring special guest Heidi Diercks, a retired educator, and life coach! Check out Heidi's coaching nuggets here :chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/https://mail.google.com/mail/u/0?ui=2&ik=89c50e1d3a&attid=0.1&permmsgid=msg-f:1826500568311074330&th=19590896f43b0e1a&view=att&zw&disp=inline&acrobatPromotionSource=GmailNativeViewer Watch on Spotify: https://creators.spotify.com/.../Lets-Get-Gritty-Podcast... #drindiawhite #grit #tedx #lifecoach #education
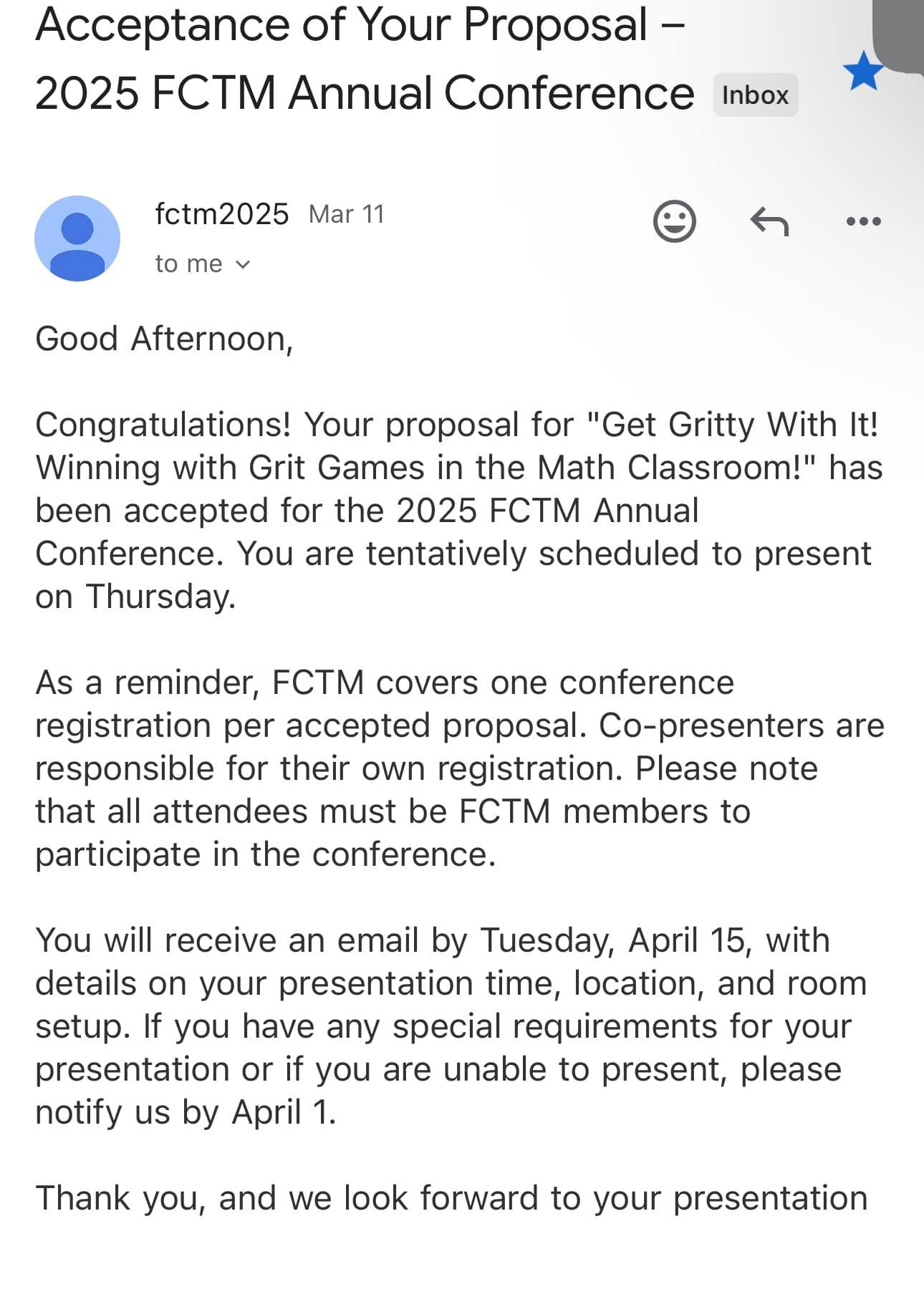
By India White
•
March 18, 2025
🌟 Super grateful to announce that I’ve been selected to speak at FCTM this year! 🎉 Let’s dive into the topic of grit and its importance in education! 💪✨ Be sure to register by visiting their website. A huge thank you to the FCTM leaders for this incredible opportunity! 🙌 #DrIndiaWhite #Grit #TEDx #Math #Educators #Teachers #Students #FCTM #NCTM #NCSM
Contact Us
Thank you for contacting us.
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Oops, there was an error sending your message.
Please try again later.
Please try again later.
© 2025
India White, All Rights Reserved. Powered By Automation Links
Terms of Us | Privacy Policy | About
